THE TIME OF ARCHITECTURE
The Origins –
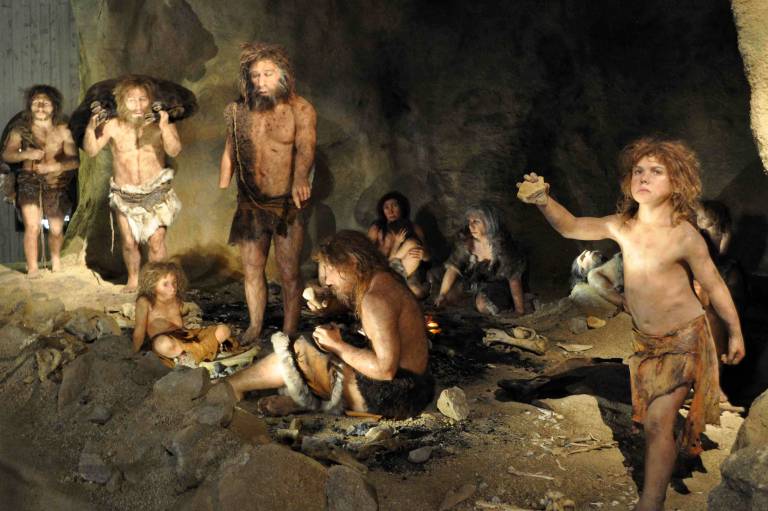
There is evidence that Homo Erectus constructed 50-foot-long branch huts with stone slabs or animal skins for floors



1.6M-200,000 BC
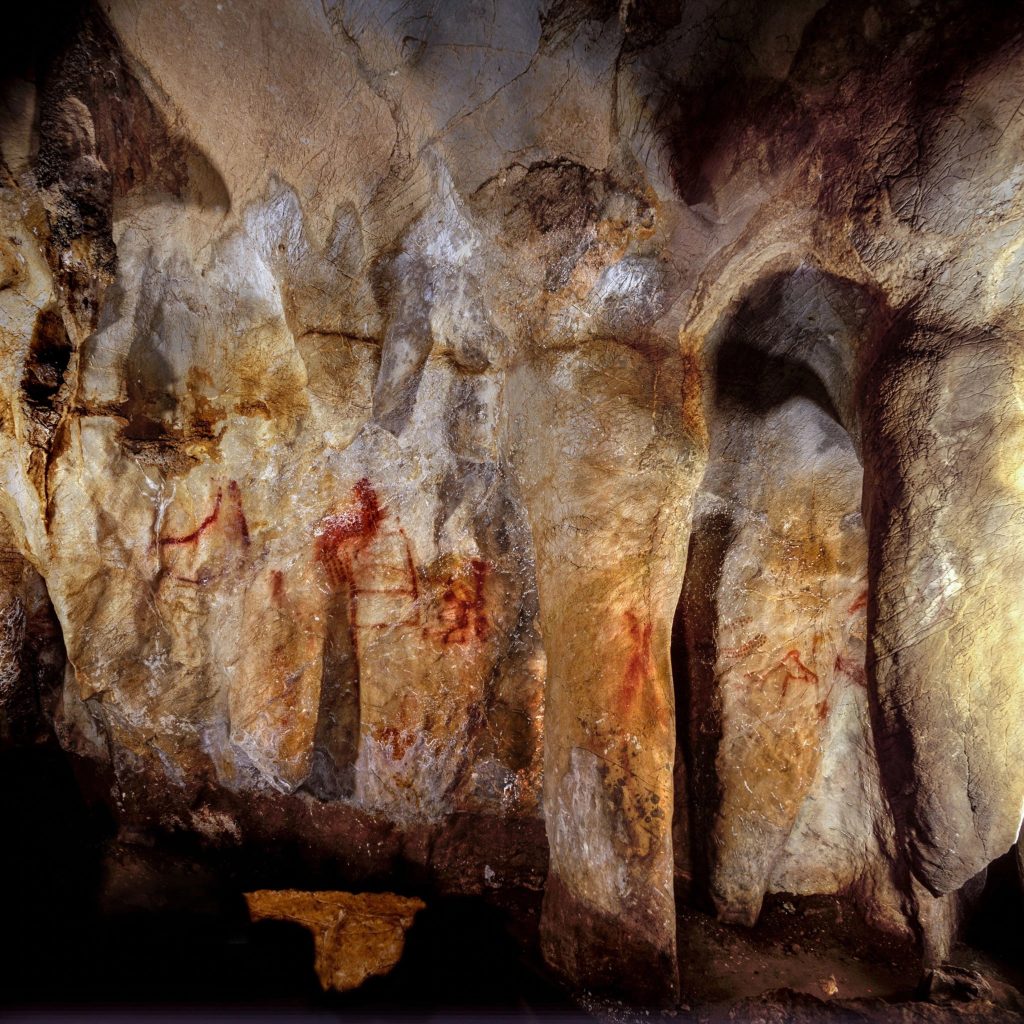




8,000 BC Neolithic –
They typically house only had one door and were made from mud brick


6,500 BC

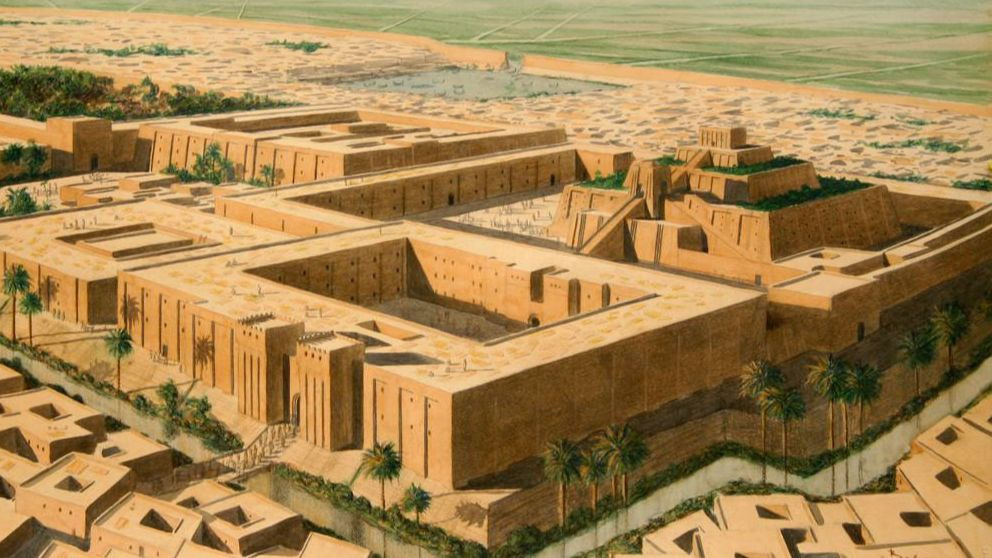
Mesopotamia –
The Mesopotamia region was famous for ziggurats, structures much like pyramids but slightly different in shape and not as massive


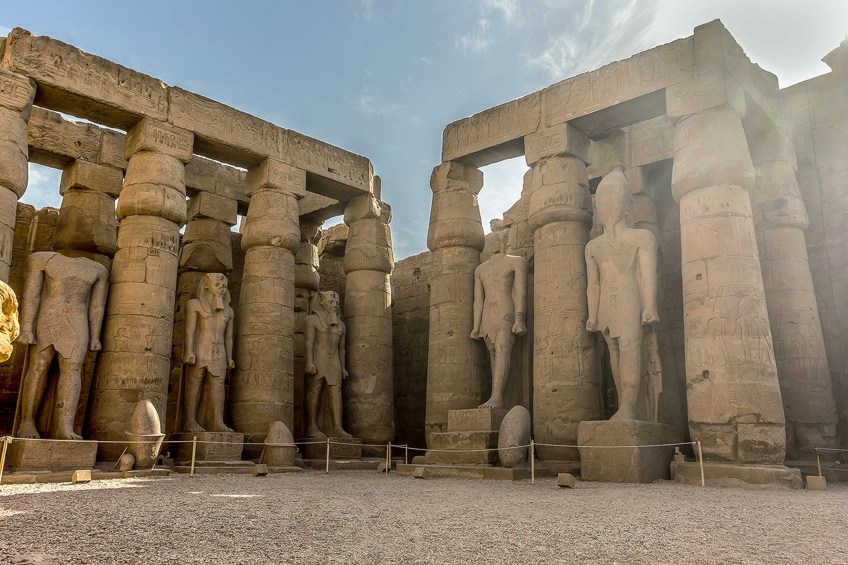
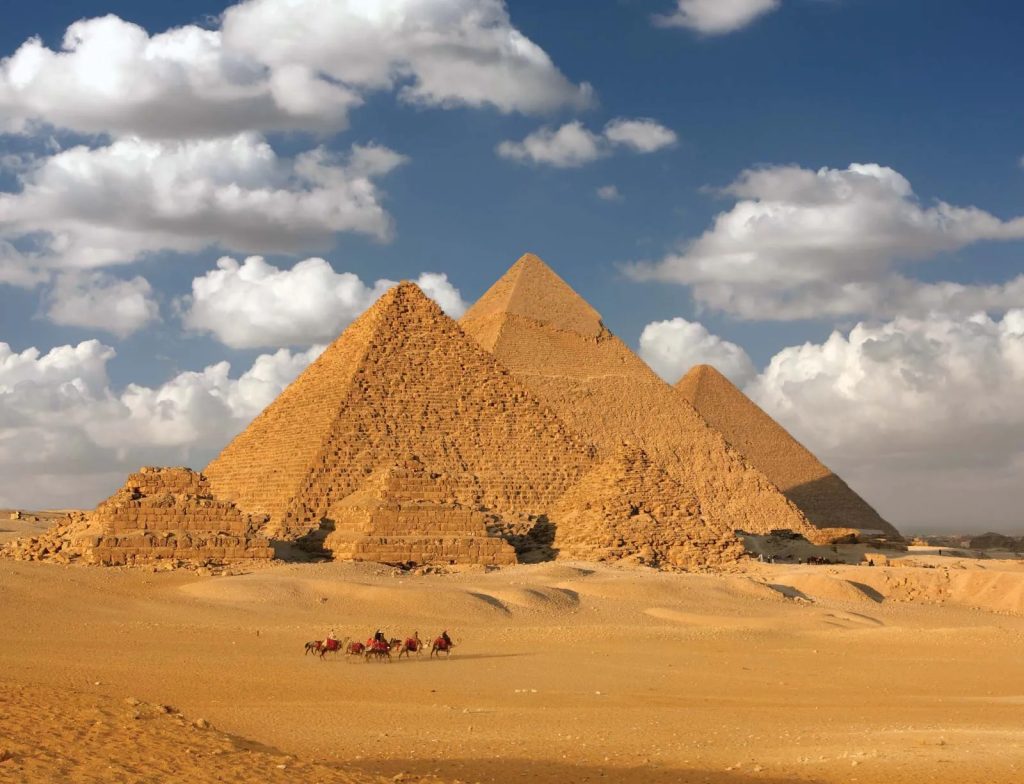
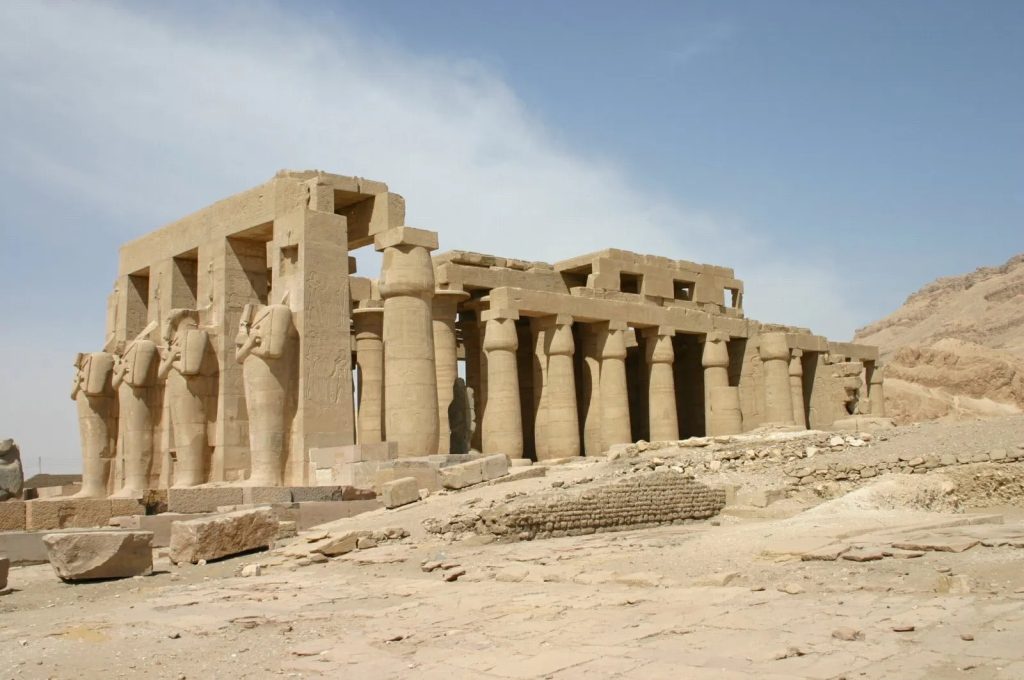
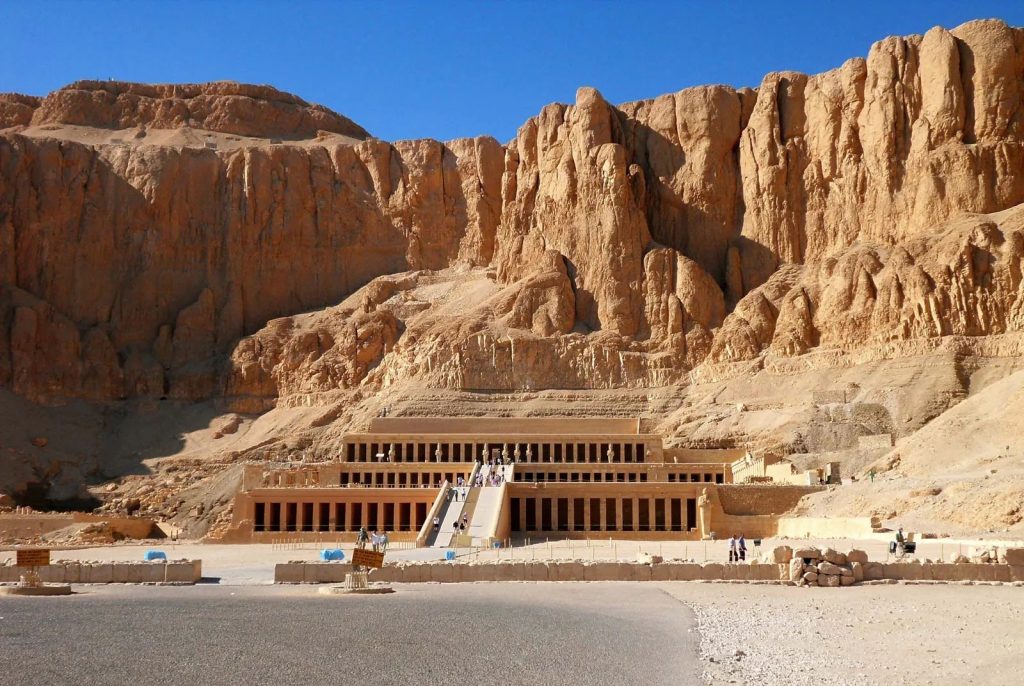
Egypt –
Egyptian architecture developed since 3000 BC and characterized by massive walls covered with hieroglyphic and pictorial carving, flat roofs, and structures such as the mastaba, obelisk, pylon and the pyramids. Houses were built of clay or baked bricks






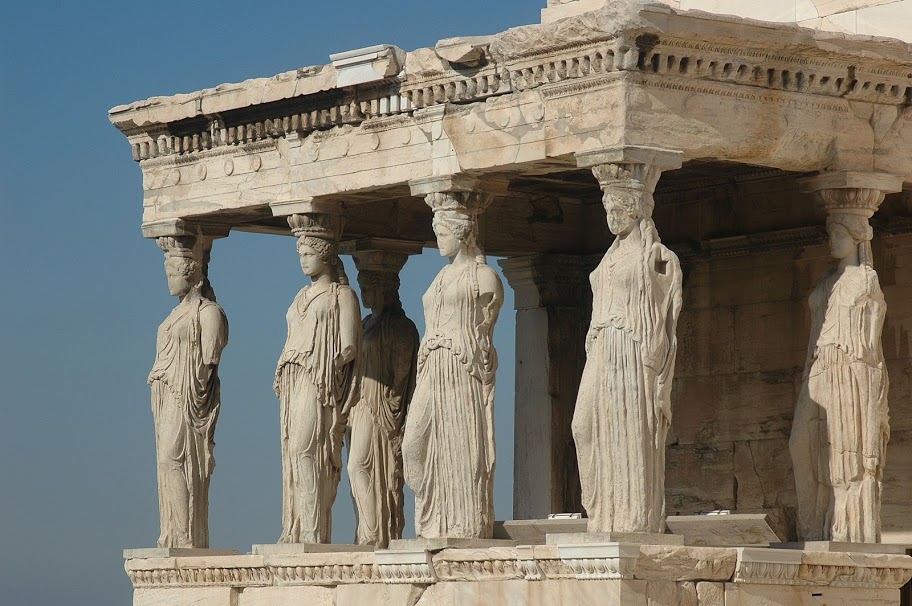
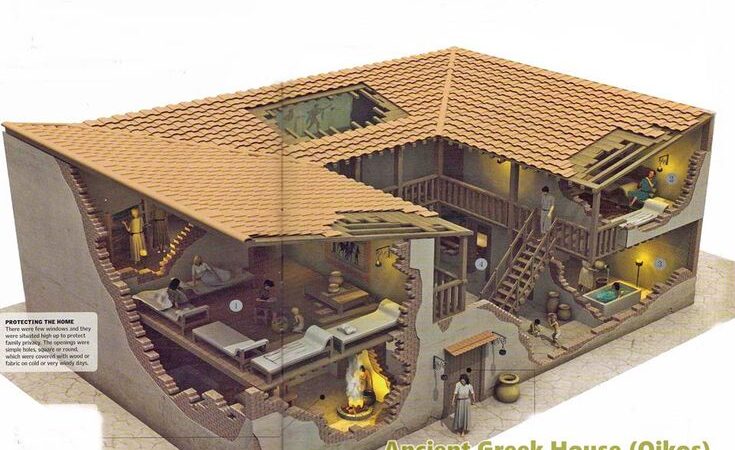
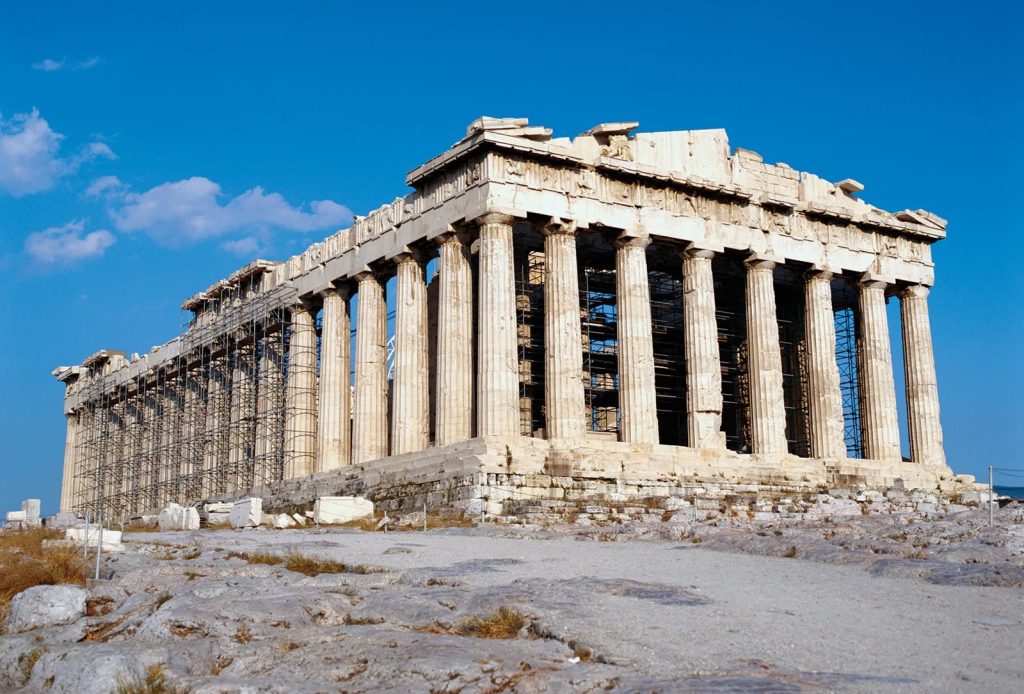
1,200 BC Greece –
Greek architecture is known for tall columns, symmetry, harmony, and balance. The Greeks built all sorts of buildings. The main examples of greek architecture that survive today are the large temples that they built to their gods





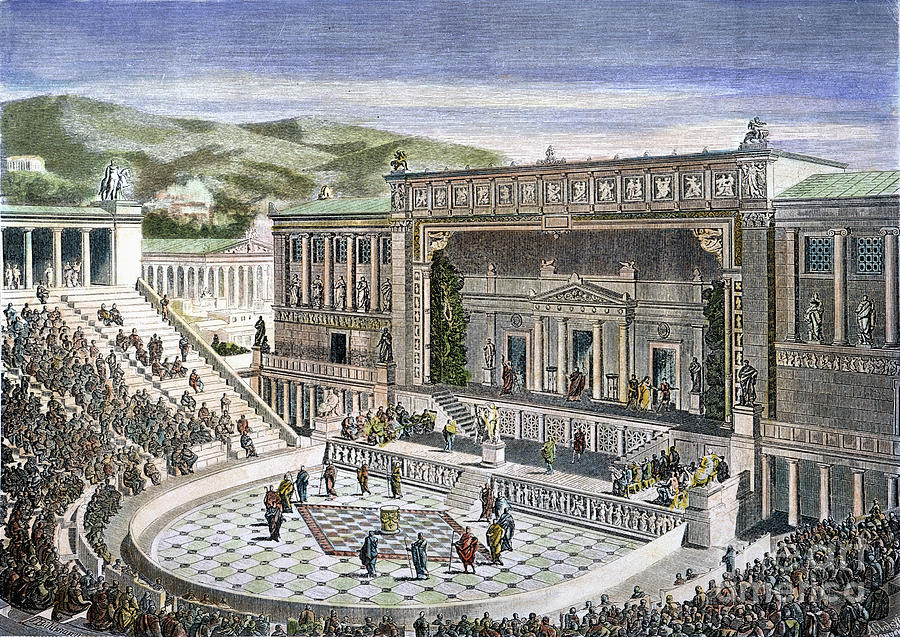





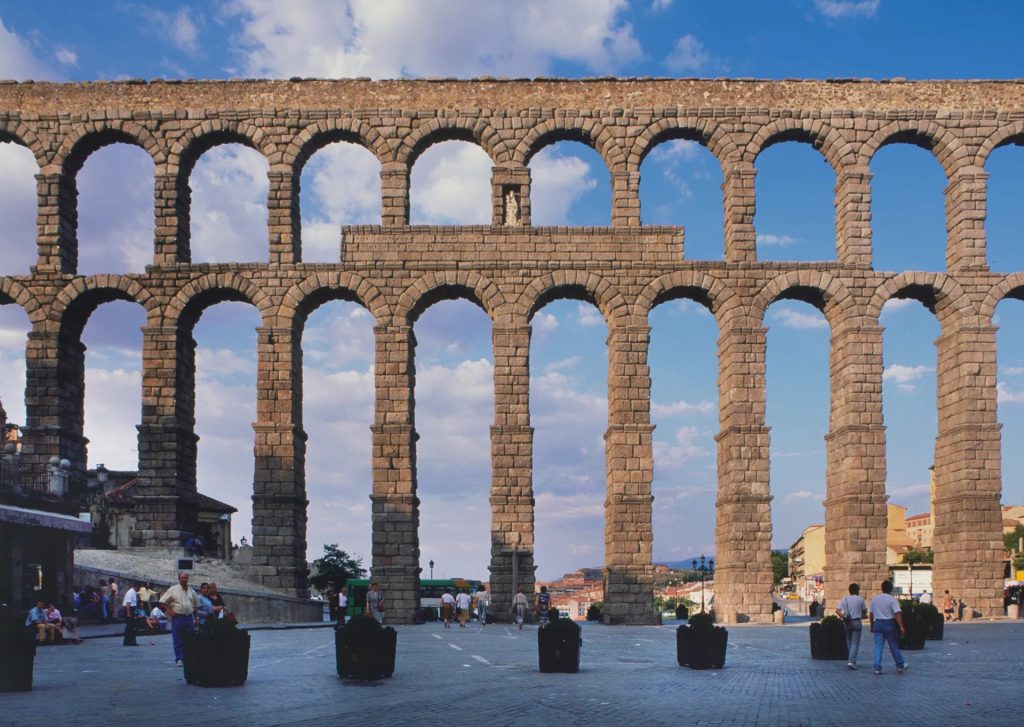
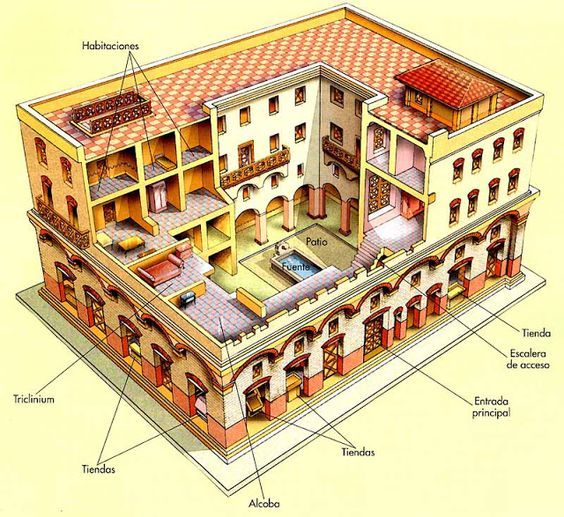
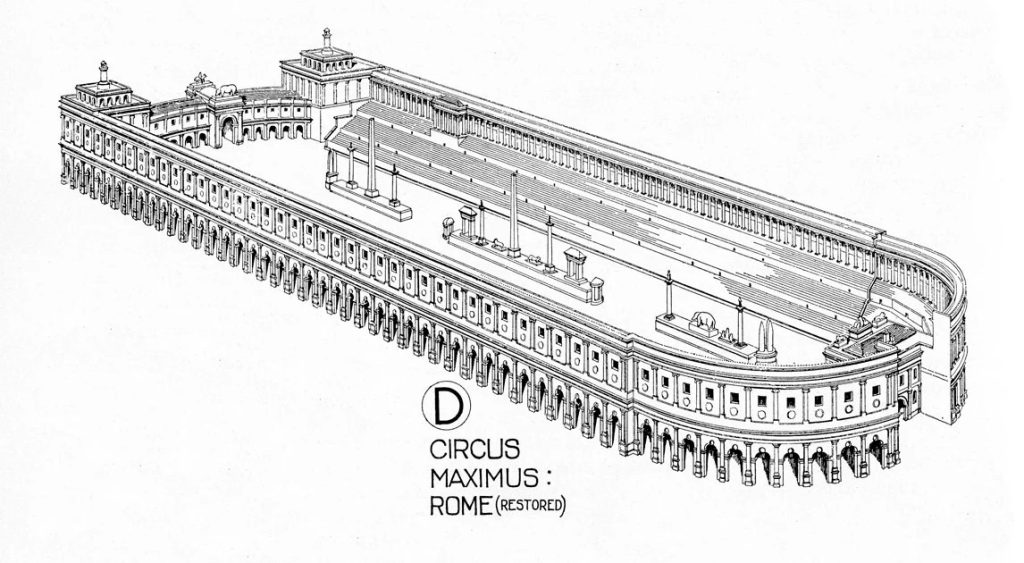
1,100 BC Romance –
A characteristic feature of Roman design was employing arches and constructed with post and lintel. Although at first tentatively employed in the spaces between the classical columns, the arch eventually came to be the most important structural element






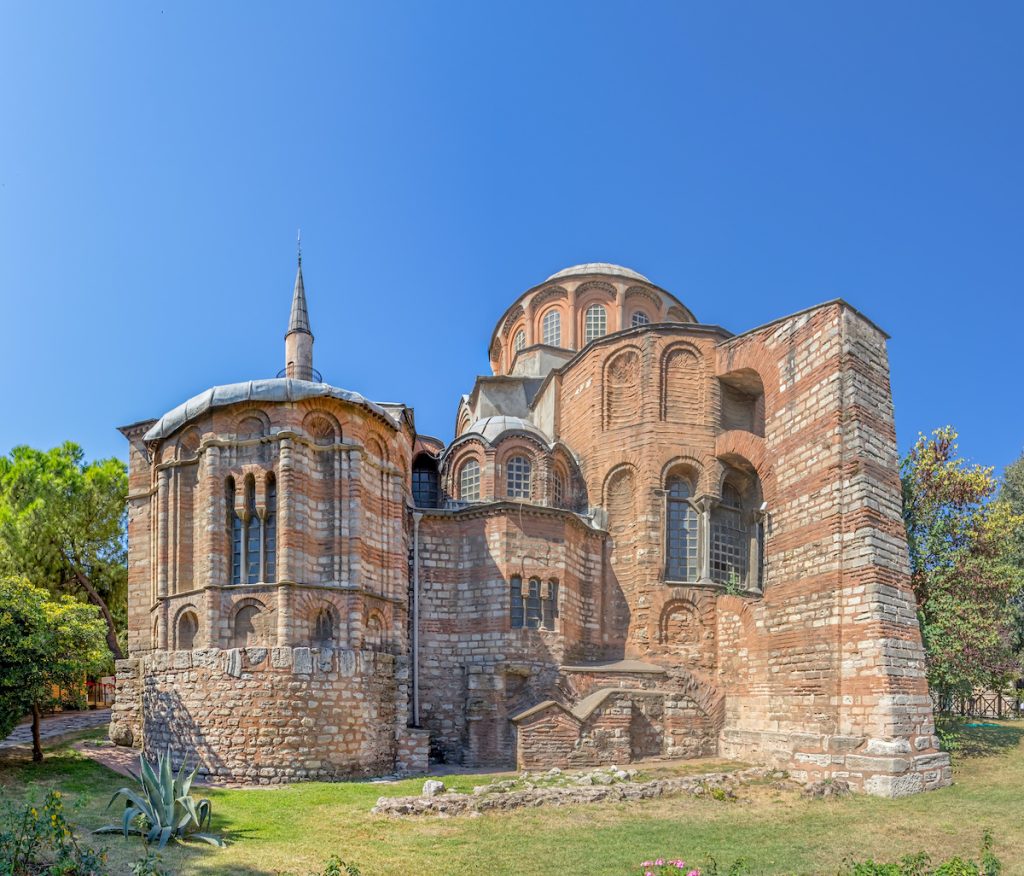
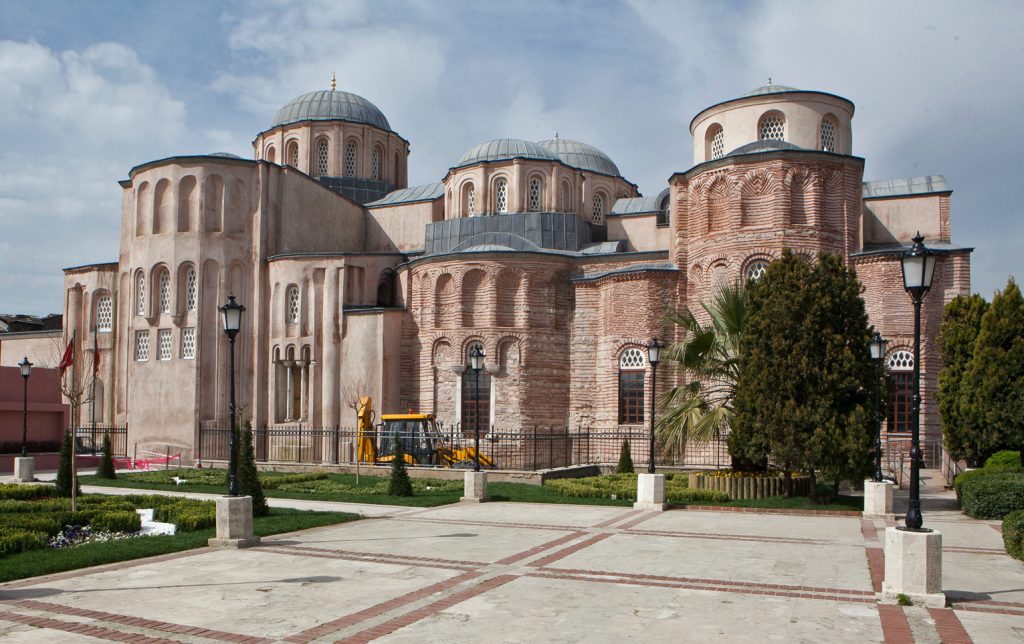
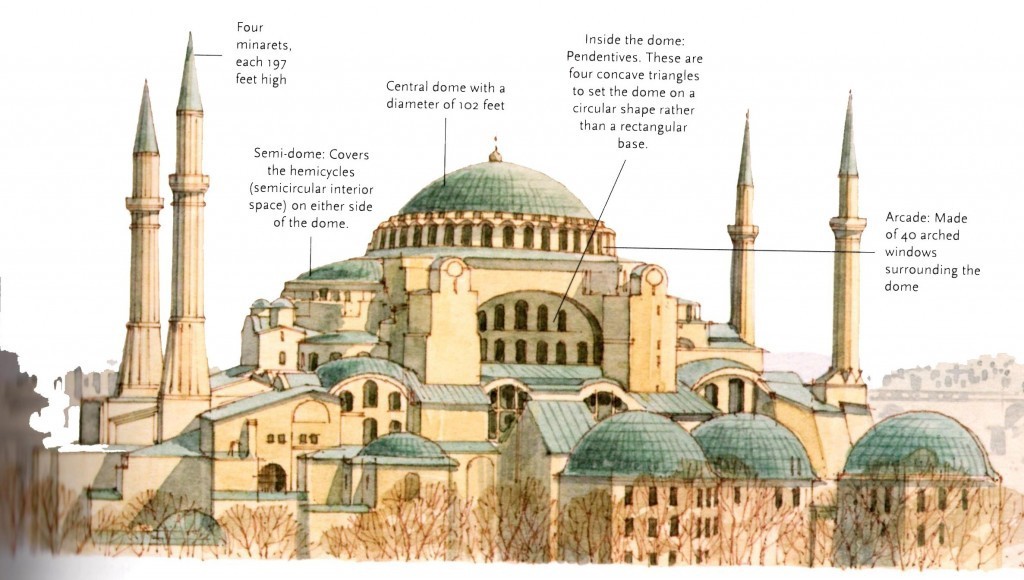
Byzantine – 5th century –
Byzantine architecture is a style of building that flourished under the rule of Roman Emperor Justinian between A.D. 527 and 565. In addition to extensive use of interior mosaics, its defining characteristic is a heightened dome, the result of the latest sixth-century engineering techniques



Pre-romanesque –
It can be divided into three periods, pre-romanesque and early romanesque architecture had thick rubble walls, smaller windows, vault-less roofs, and rhythmic ornamental arches while mature romanesque architecture had more refined style and increased use of the vault and dressed stone
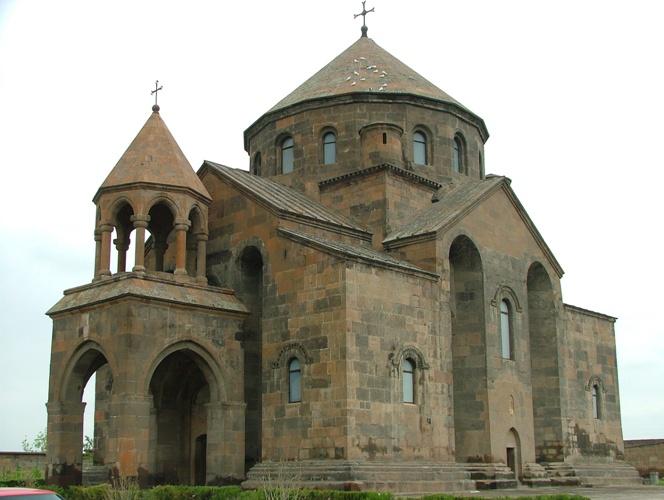






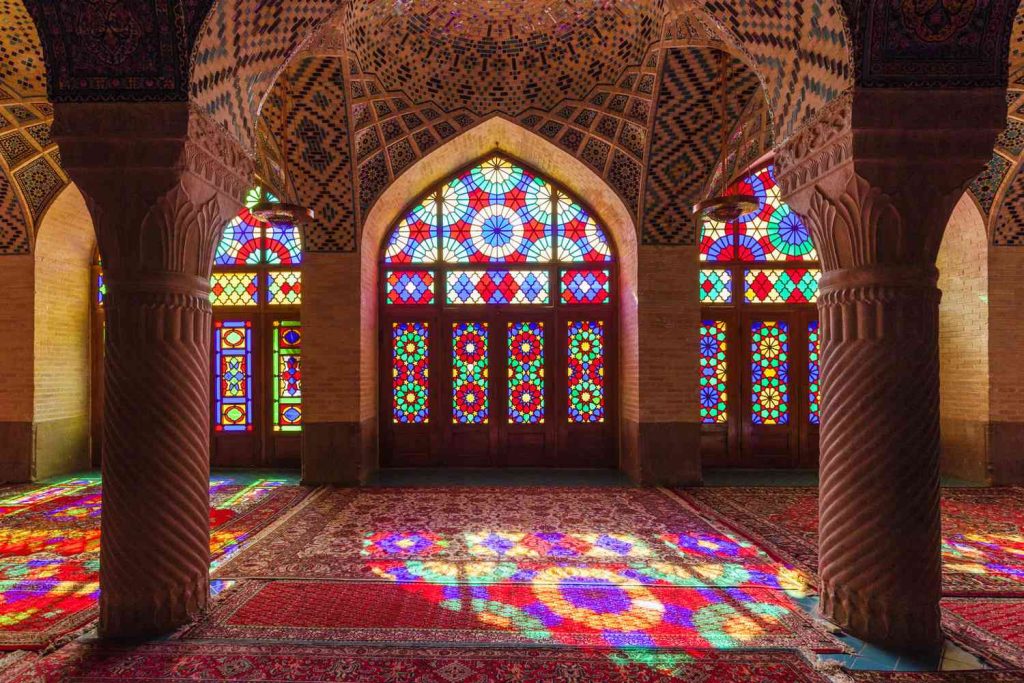
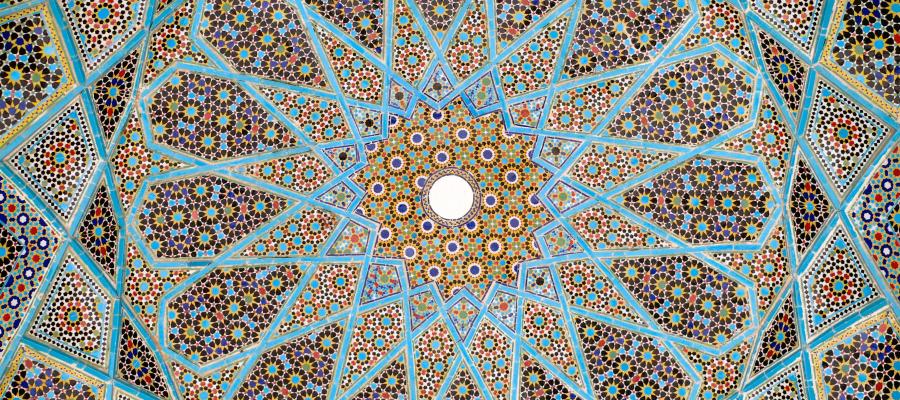
Islamic –
Islamic Decorations include geometrical patterns, floral motifs, and calligraphy. The Roman, Greek, and Sasanian cultures have inspired Islamic architecture to use symmetrical patterns. Islamic art and architecture commonly feature the eight-pointed star patterns
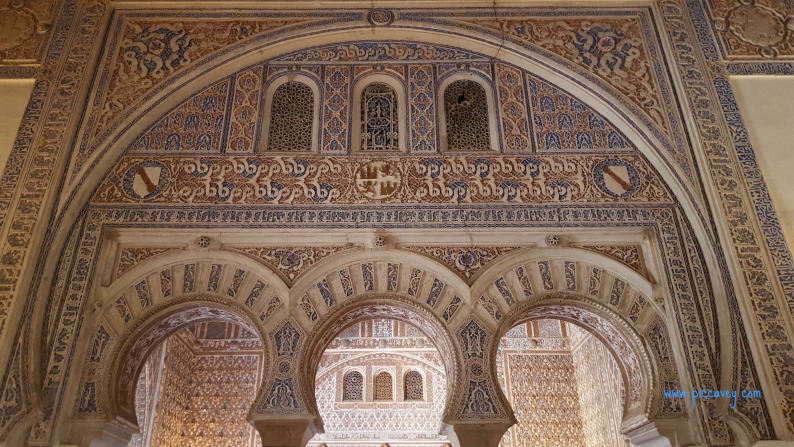




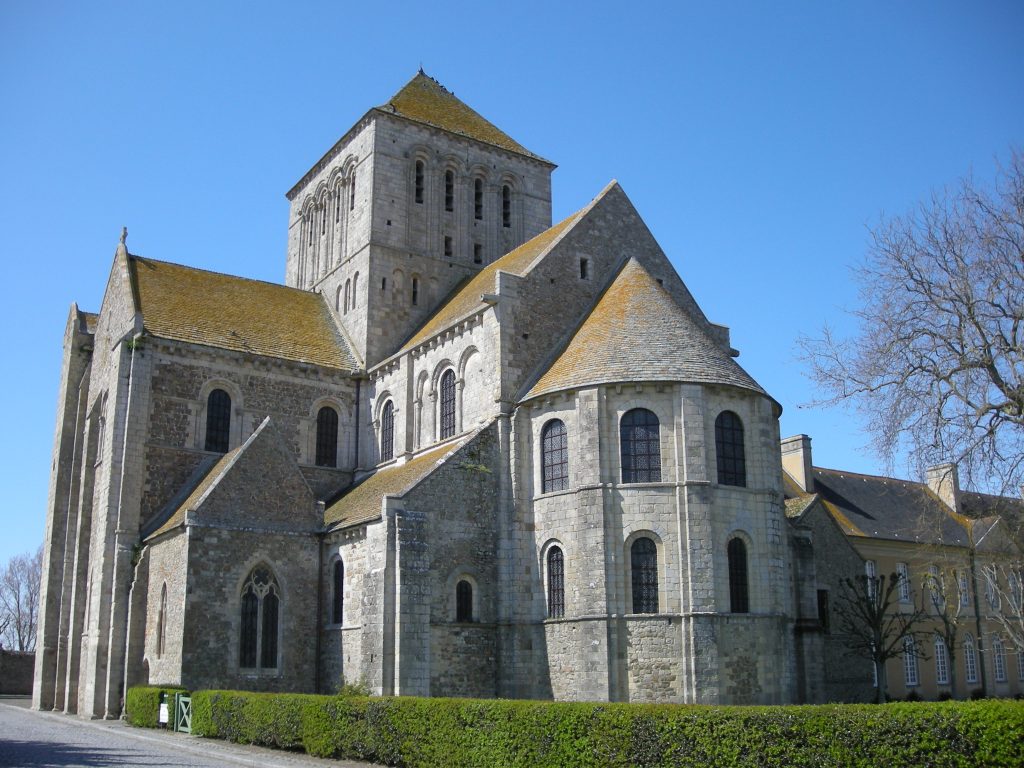
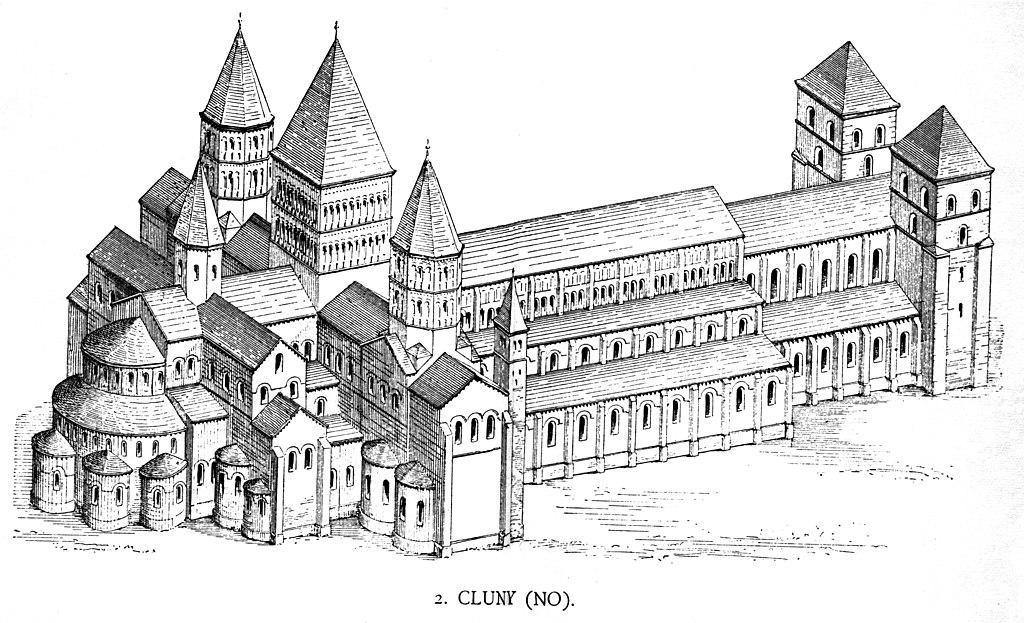
Romanesque –
Combining features of ancient Roman and Byzantine buildings and other local traditions, Romanesque architecture is known by its massive quality, thick walls, round arches, sturdy pillars, barrel vaults, large towers and decorative arcading



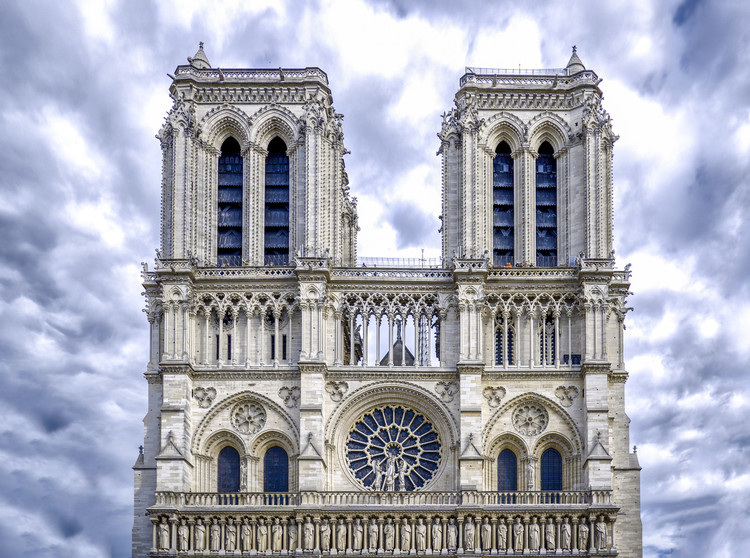
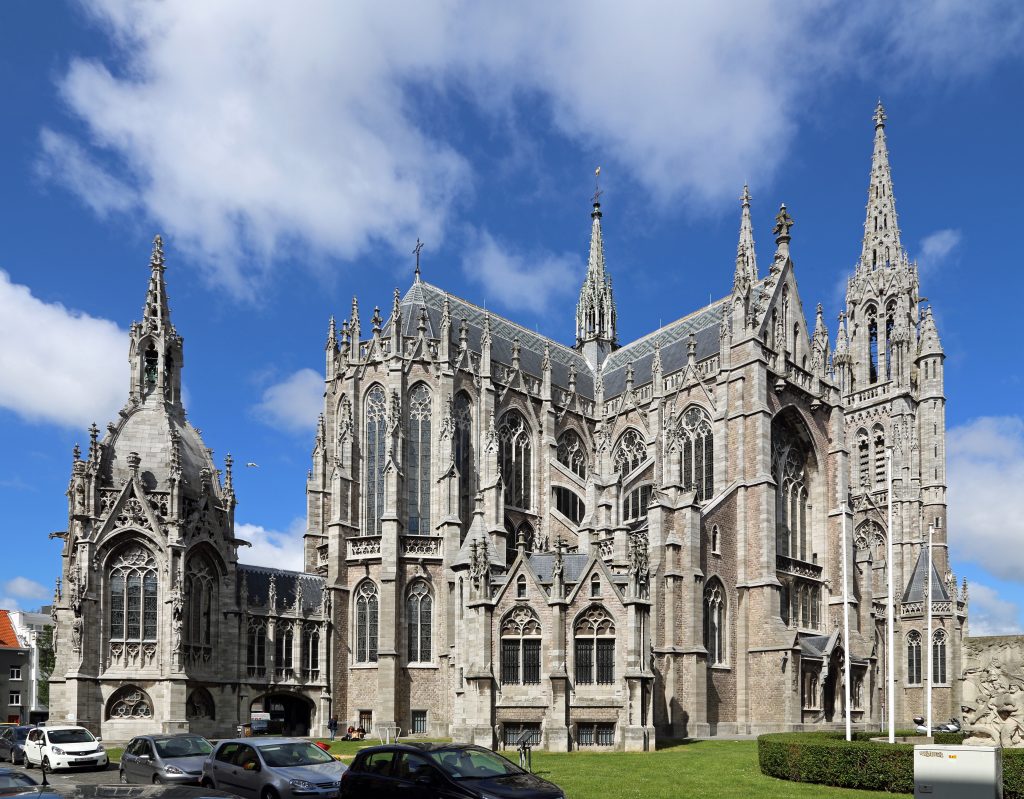
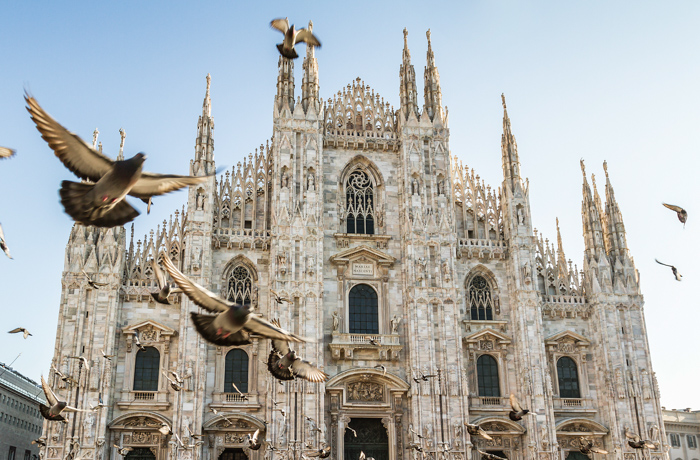
Gothic –
Architectural style in Europe that lasted from the mid-12th century to the 16th century, particularly a style of masonry building characterized by cavernous spaces. It is often characterized by 5 key architectural elements: large stained glass windows, pointed arches, rib vaults, flying buttresses, and ornate decoration.
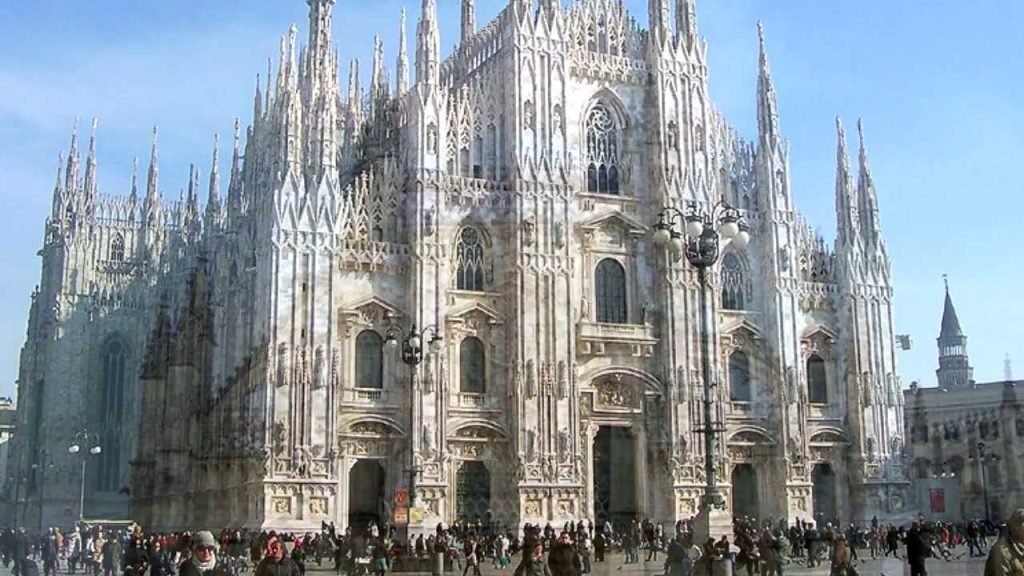
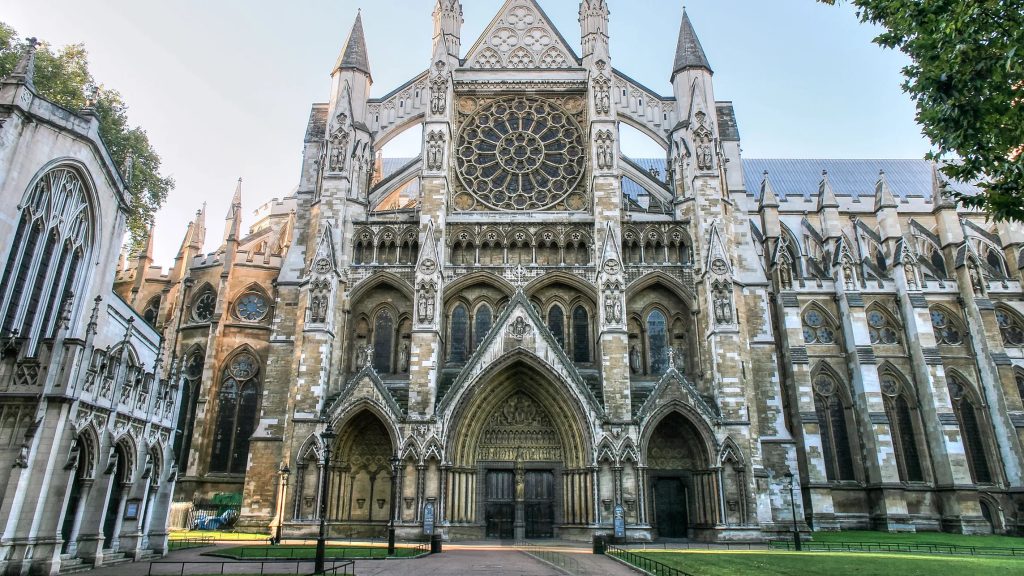






Renaissance –
The key features of Renaissance architecture are the use of the classical orders, mathematically precise ratios of height and width, symmetry, proportion, and harmony. Columns, pediments, arches, and domes are imaginatively used in buildings of all types
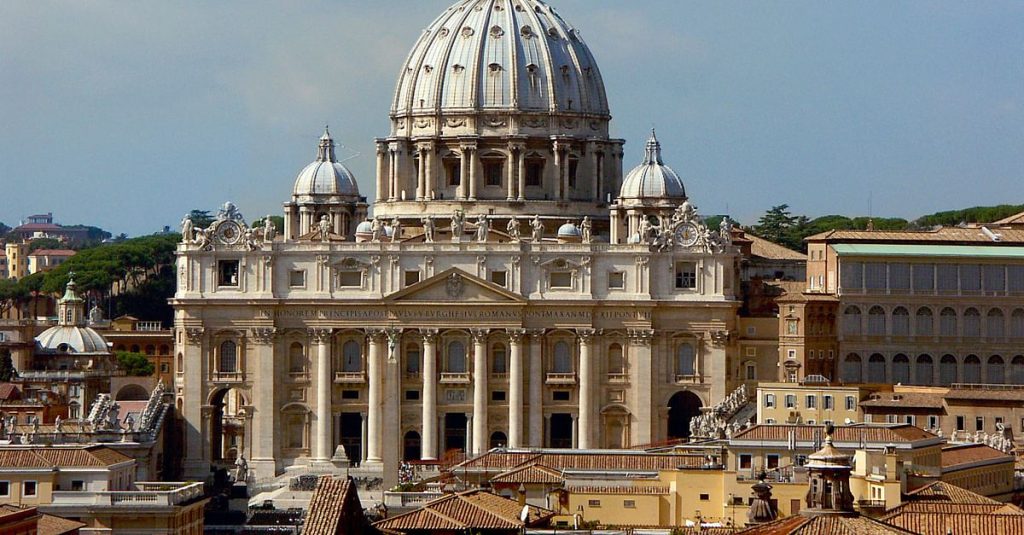
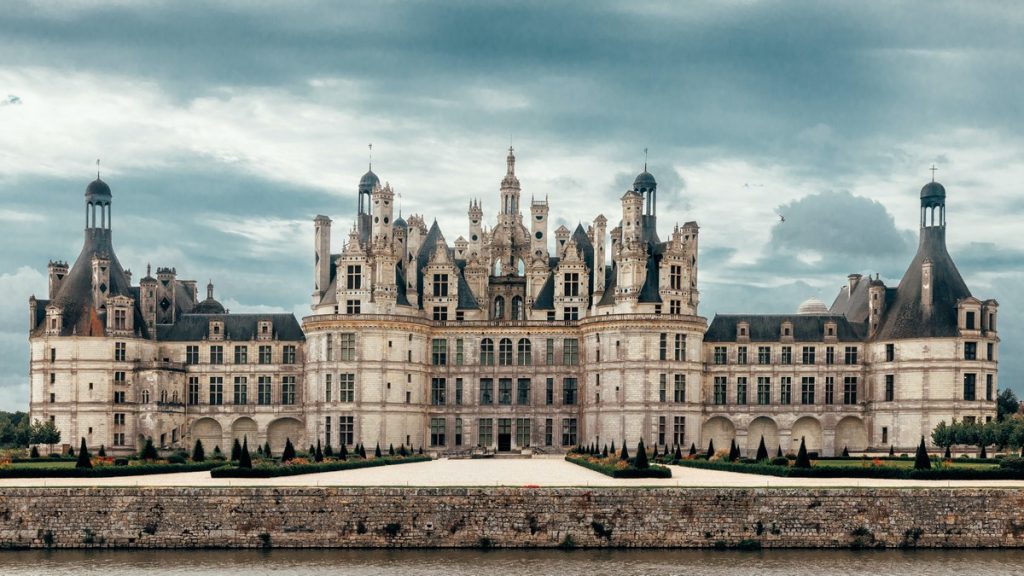
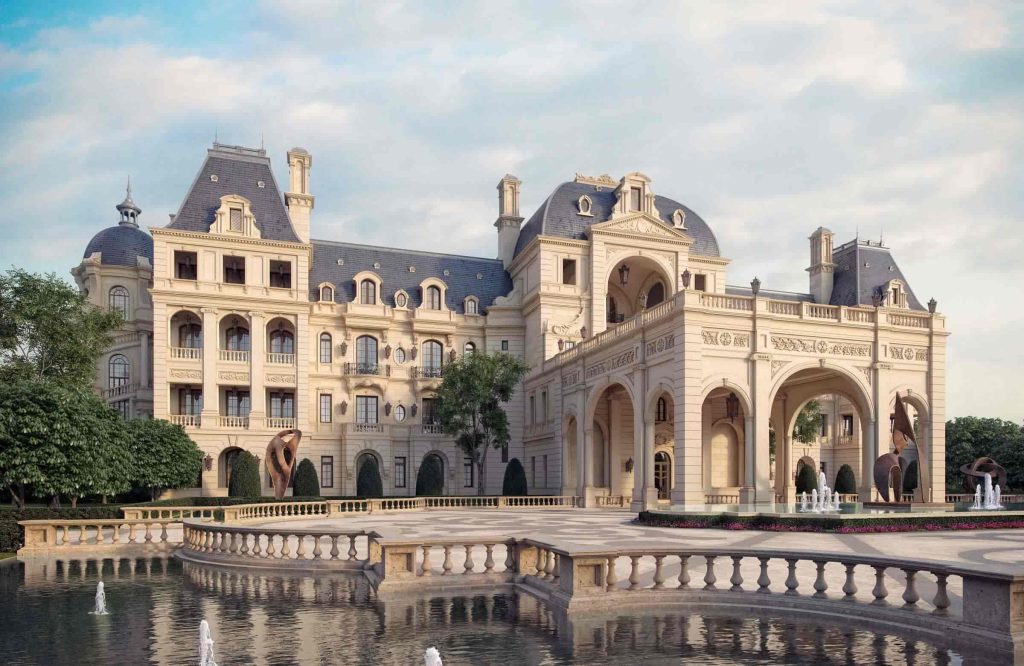
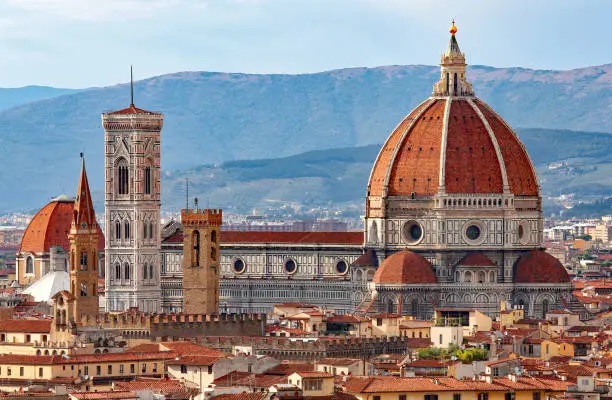







Baroque –
Is characterised by dynamic designs and complex architectural plan forms. Intended to heightened feelings of motion and sensuality, and frequently based on the oval. Originating in Italy, its influence quickly spread across Europe and it became the first visual style to have a significant worldwide impact.
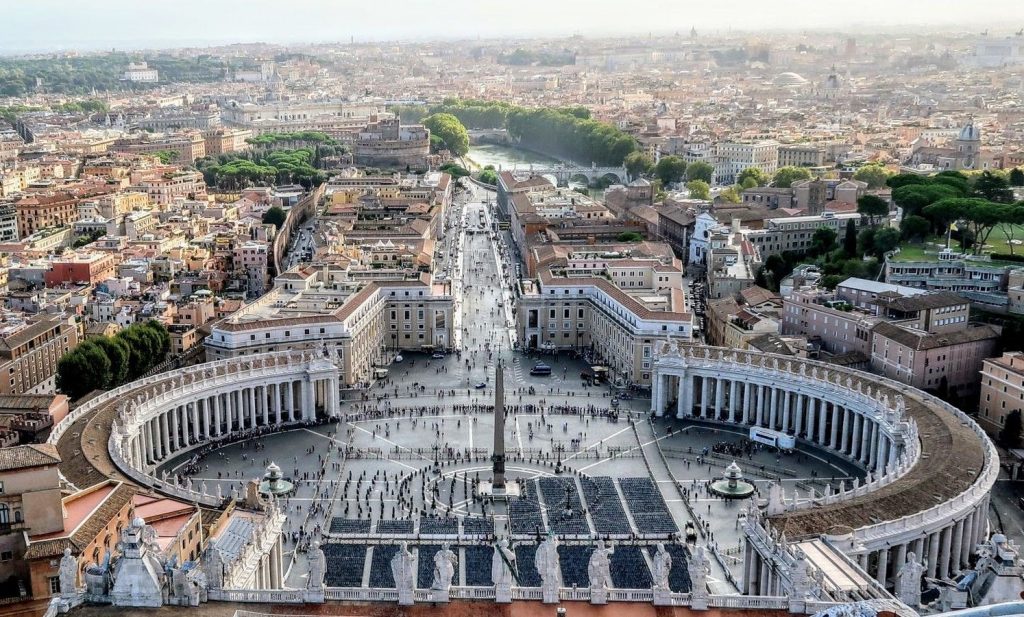
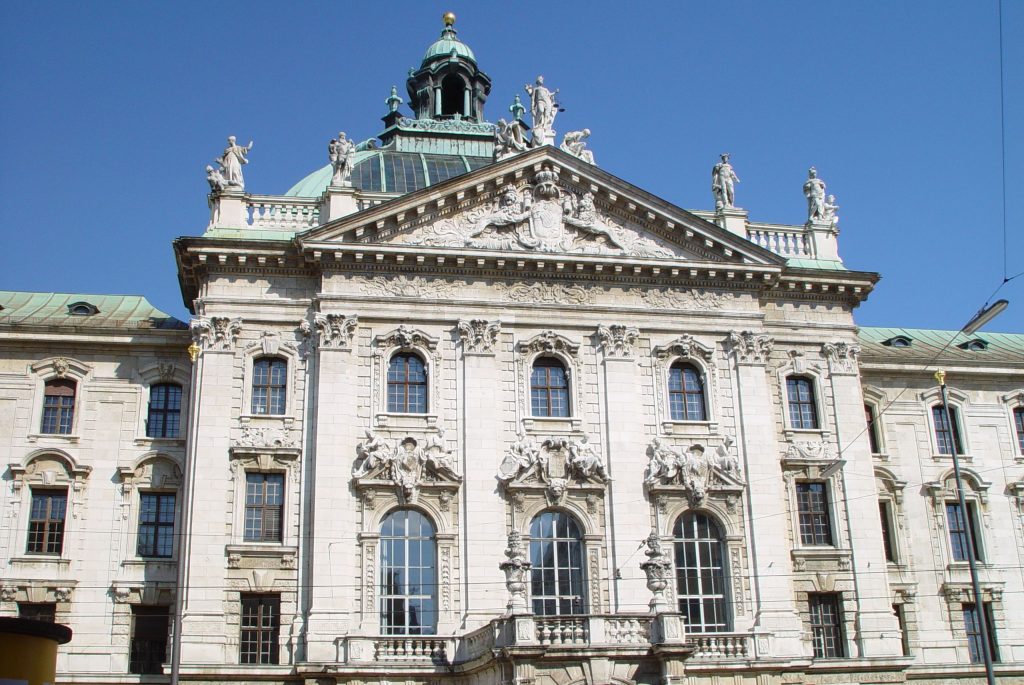





Neoclassic –
Neoclassical architecture is characterized by grandeur of scale, simplicity of geometric forms, greek or roman details, dramatic use of columns, and a preference for blank walls
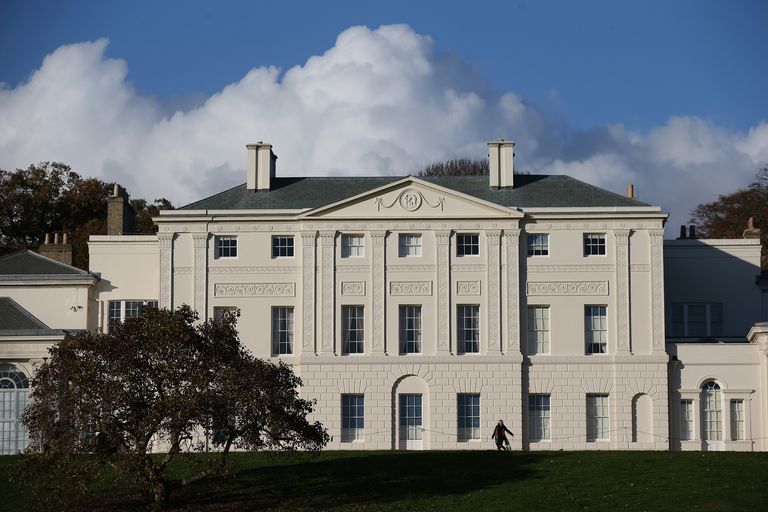
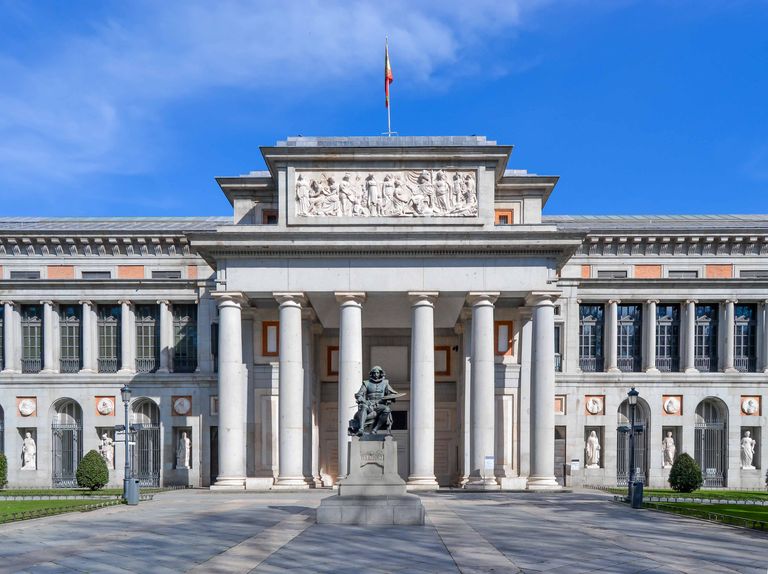
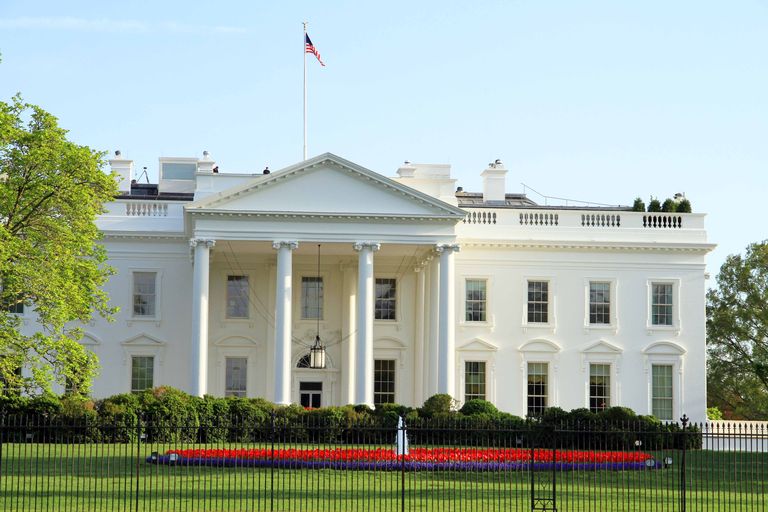
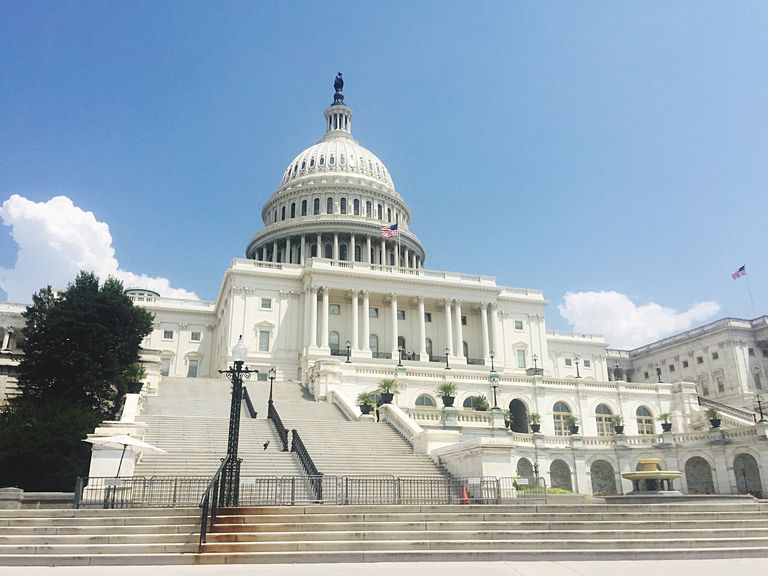
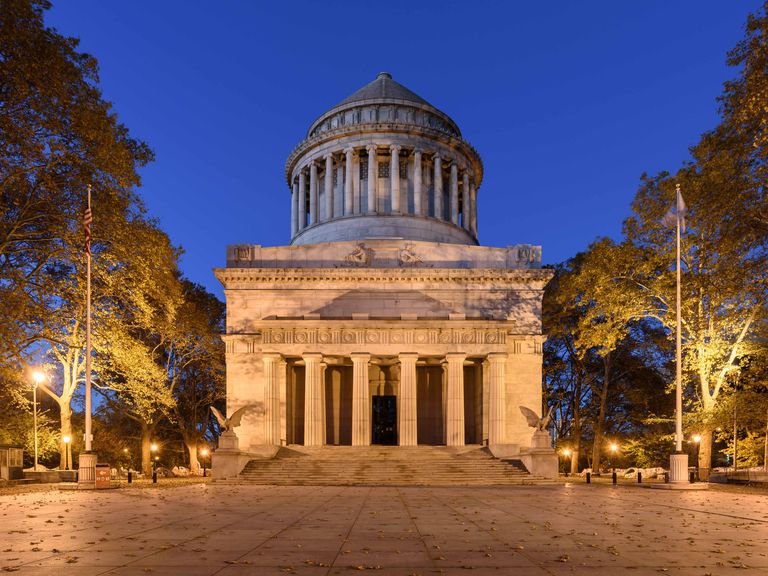
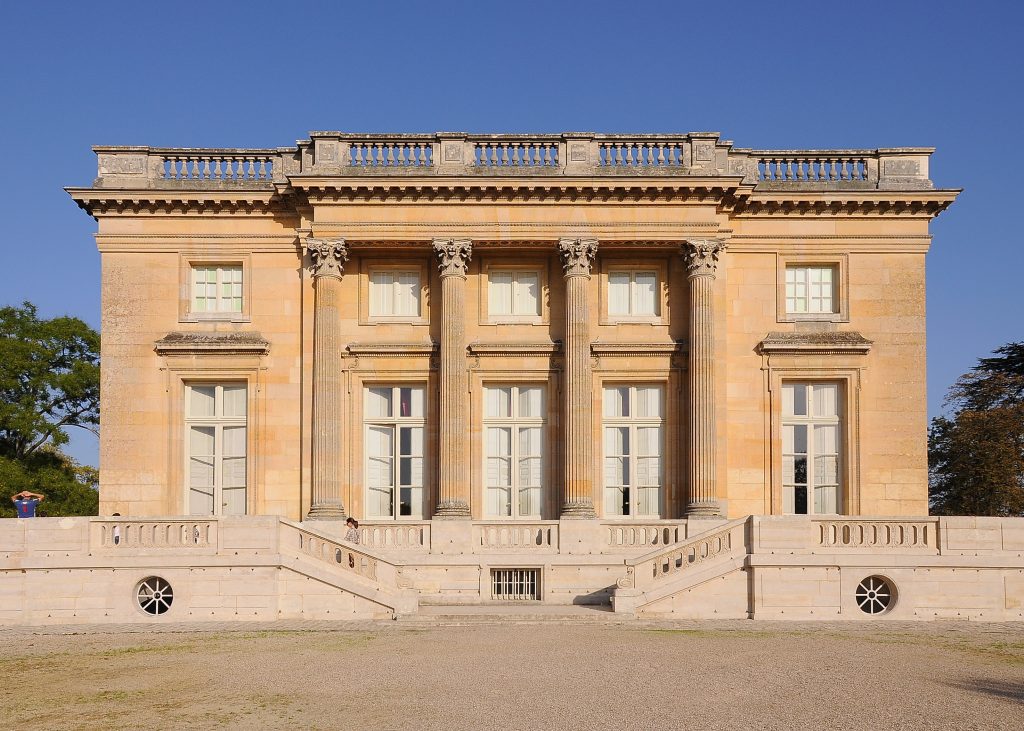







19th century –
The use of a variety of historical styles and the development of new materials and structural methods
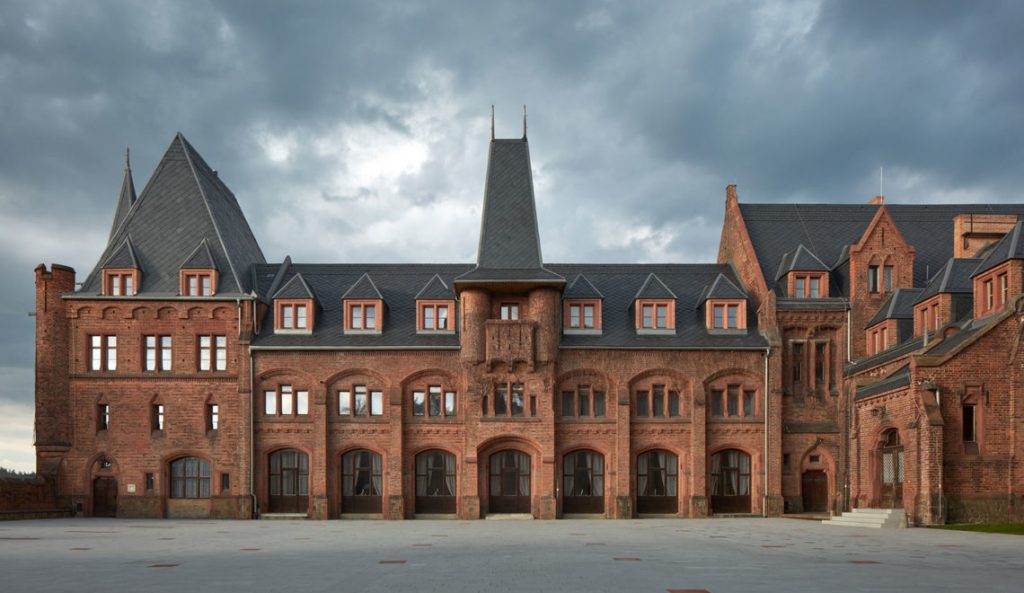
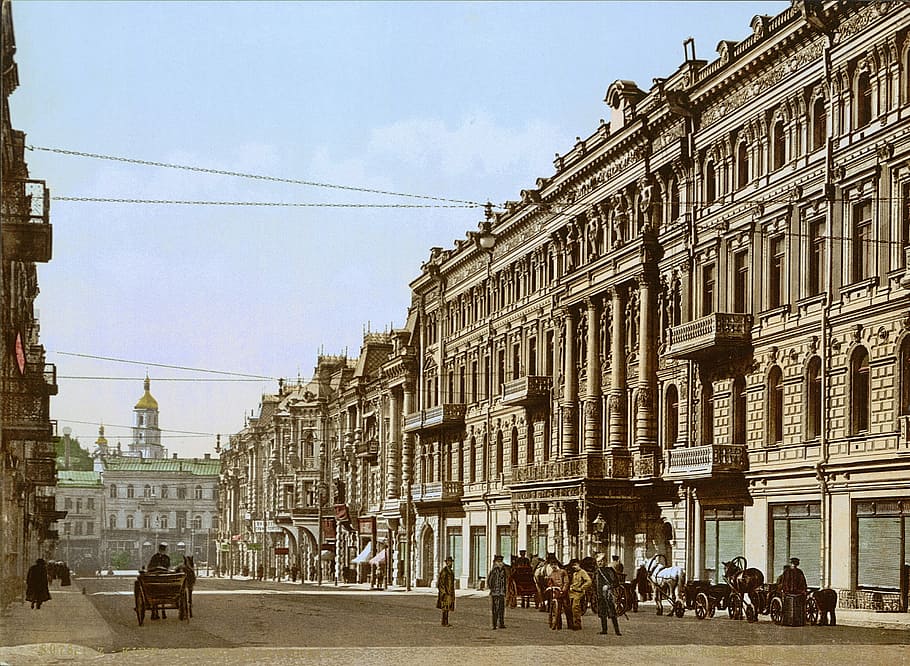
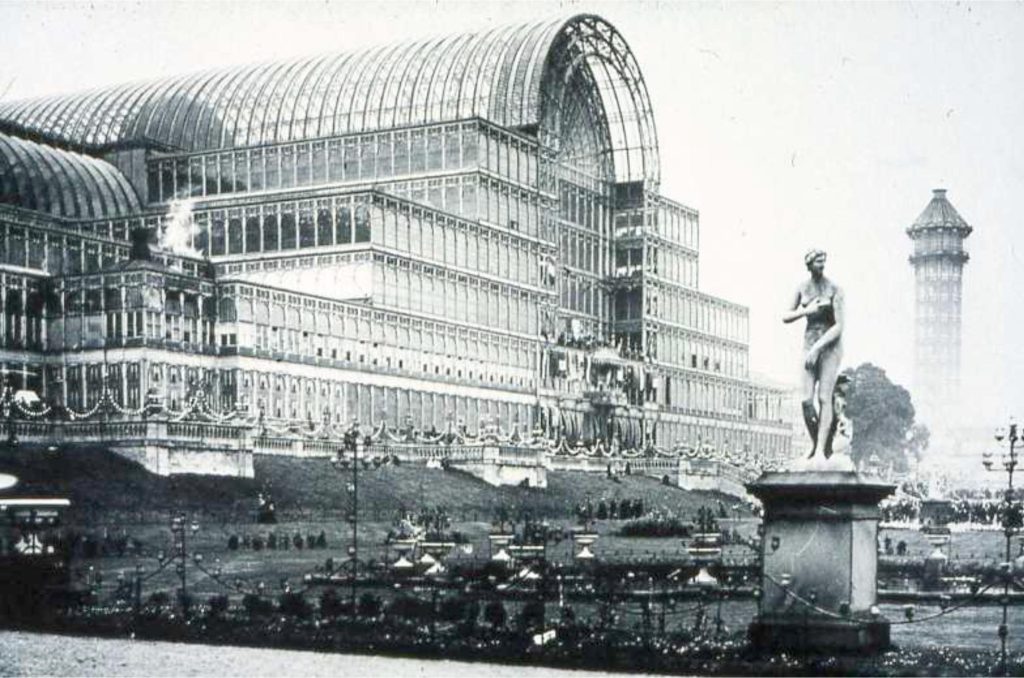
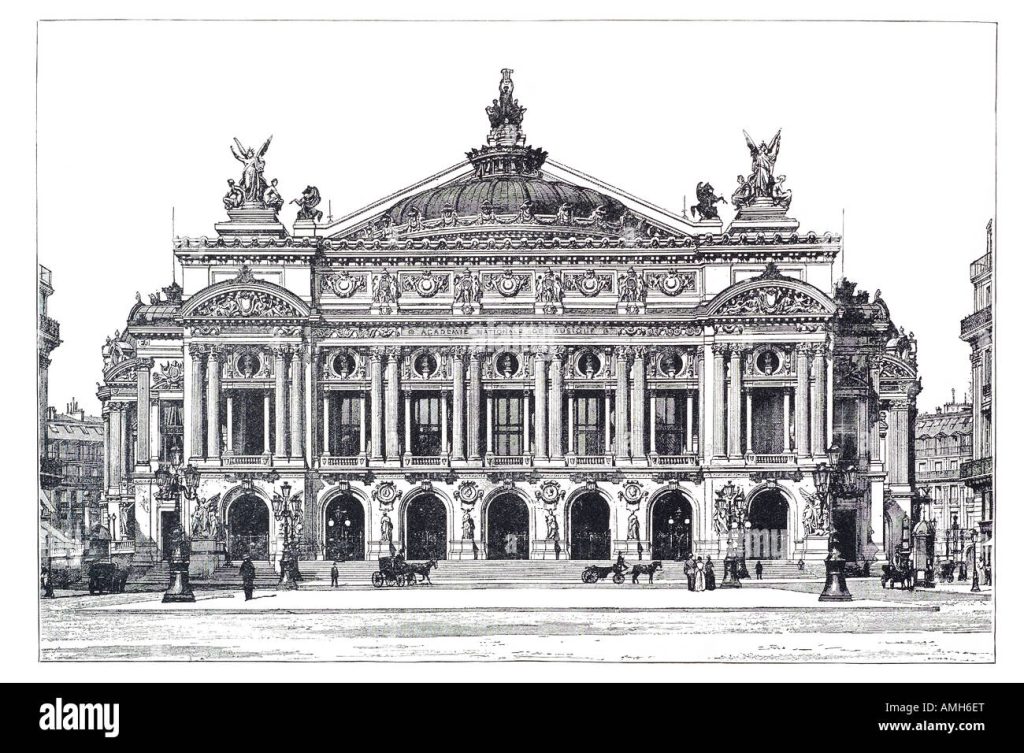



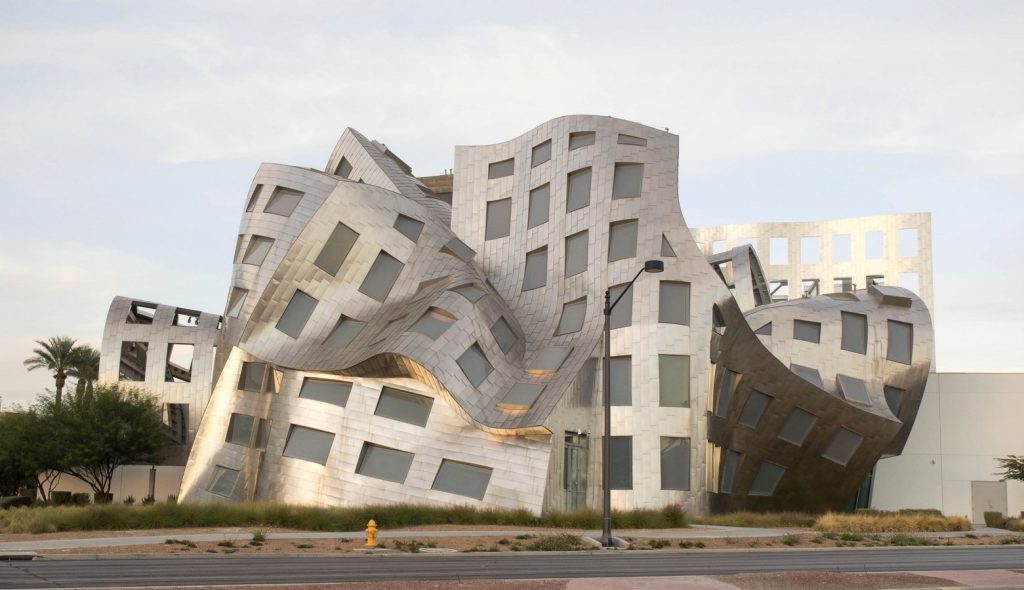
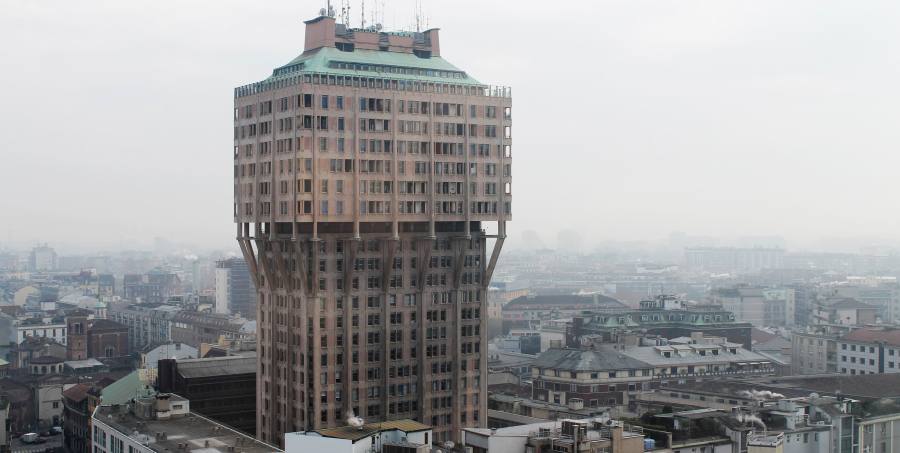
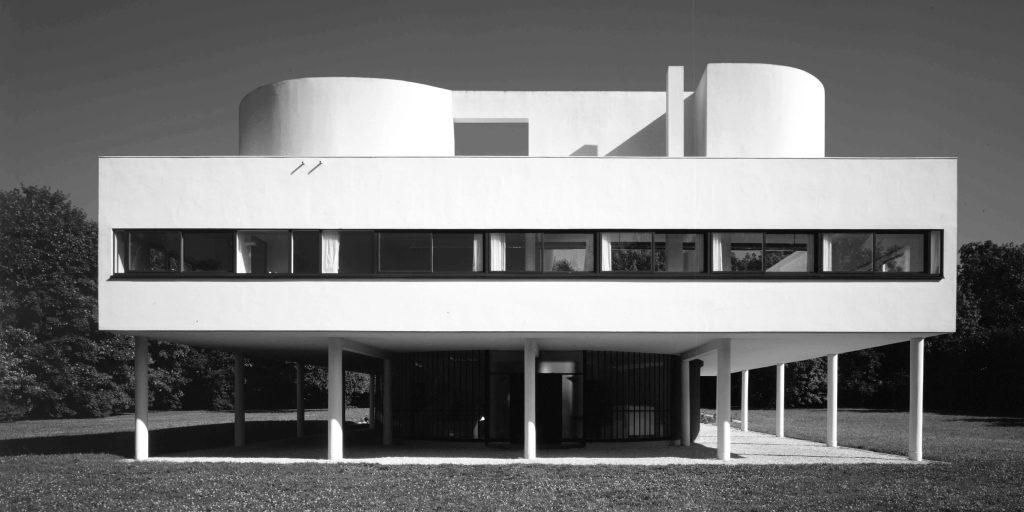
20th century –
Rationalism is considered the main architectural style of the 20th century. The Bauhaus style, the Soviet brutalism and more… Use of modern materials such as concrete, glass, curtain walls and metal, rectangular forms, repetitive modular forms, ribbon windows and open interior spaces








